.
S O U R C E : MedicalXpress
B E H I N D P A Y W A L L P R I M A L S O U R C E : Science Translational Medicine (An embryonic CaVβ1 isoform promotes muscle mass maintenance via GDF5 signaling in adult mouse)
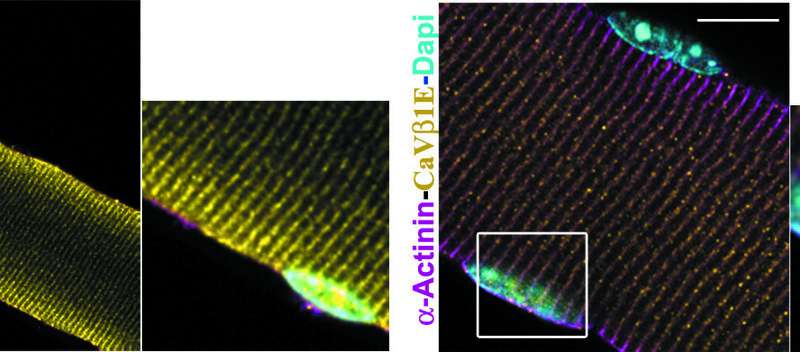
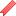
Focus on the CaVbeta1E protein that activates the factor GDF5. This mechanism promotes the prevention of sarcopenia by maintaining the muscle mass and strength of aged mice Credit: France Pietri-Rouxel, Sestina Falcone
Skeletal muscle is the most abundant tissue of the human body (about 40%) and it plays essential role in locomotion and vital functions (heart rate, breathing). During aging, in a large majority of individuals a loss of muscle mass, quality and strength occurs: this is called sarcopenia. This state, leading to disability and dependence, was declared as a disease in 2016 by the World Health Organization.
By studying the young and aging muscles in mice, researchers from the Myology Research Center (Sorbonne Universite-Inserm) of the Institute of Myology identified a protein, CaVbeta1E that activates the factor GDF5. This mechanism promotes the prevention of sarcopenia by maintaining the muscle mass and strength of aged mice. The team discovered the CaVbeta1E protein in humans and showed that its expression correlated with the loss of muscle mass of the elderly. Published today in Science Translational Medicine, this study opens a new field of activity in the development of therapeutic strategies against the muscular decline associated with aging.
Sarcopenia is defined by a progressive and generalized loss of mass, strength and quality of the entire musculature from the age of 50, which may ultimately lead to a decrease of more than 30% of the initial muscle mass. Its consequences are numerous: increased risk of falls (the leading cause of death related to an injury in people over 65), increased length of hospital stay, infectious risks, dependence. Qualified as "Disease" in 2016 by the World Health Organization, sarcopenia, currently affects about one in five European over 55 year old (30 million by 2045): it is a major public health issue.
The muscle mass depends on the innervation and the excitation (nerve)-contraction (muscle) coupling. It can vary according to environmental changes, increase (hypertrophy), as after muscle training, or decrease (atrophy) as during prolonged immobilization, nerve damage, in a pathological context or during aging. The muscle's response to atrophy is the establishment of molecular mechanisms that tend to limit its loss.
.../...
.