AVOiD All Vitamin D Supplementation ...
Science behind vitamin D A number of studies have suggested that patients with chronic inflammatory diseases are deficient in 25-hydroxyvitamin D (
25-D) and that consuming greater quantities of vitamin D, which further elevates 25-D levels, alleviates disease symptoms.
Some years ago, molecular biology identified 25-D as a secosteroid. Secosteroids would typically be expected to depress
inflammation, which is in line with the reports of short-term symptomatic improvement. The simplistic first-order mass-action model used to guide the early vitamin studies is now giving way to a more complex description of action.
When active, the
Vitamin D nuclear receptor (VDR) affects transcription of at least 913 genes and impacts processes ranging from calcium metabolism to expression of key
antimicrobial peptides. Additionally, recent research on the
Human Microbiome shows that bacteria are far more pervasive than previously thought, dramatically increasing the possibility that the spectrum of chronic diseases is bacterial in origin.
Emerging molecular evidence suggests that symptomatic improvements among those administered vitamin D is the result of 25-D’s ability to temper bacterial-induced inflammation by slowing VDR activity. While this results in short-term palliation, persistent pathogens that influence disease progression proliferate over the long-term.
Forms and structure of vitamin D All forms of vitamin D are secosteroids, sharing a close structural and functional resemblance to steroids. The full implications of a “vitamin” acting as a steroid has yet to be fully appreciated by many in the research community. The overlap between steroids and secosteroids is key to understanding the
Marshall Pathogenesis. It explains how a “vitamin” can exert short-term palliative effects and long-term harm. Patients on the MP are advised to avoid consuming vitamin D, because of its immunomodulatory effects.
Steps for synthesis of Vitamin D There are a number of vitamin D metabolites in the body. The steps by which one form of vitamin D changes into the next are as follows:
The body has natural stores of 7-dehydrocholesterol, a cholesterol precursor.
When exposed to energy, specifically ultraviolet light, 7-dehydrocholesterol becomes pre-vitamin D3.
Pre-vitamin D3 spontaneously isomerizes to Vitamin D3 via a process called sigmatropic shift.
In addition to the endogenous production of Vitamin D3, people get D3 from animal meats. Vitamin D2 is found in plants and fungi, and is functionally similar to D3.
Vitamin D3 and D2 are hydroxylated in the liver, and becomes 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25-D).
25-D is further hydroxylated by the enzyme 1α-hydroxylase, into the main biologically active hormone 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D(1,25-D). While this reaction was originally thought to occur only in the kidneys, is now known to take place in tissues throughout the body, including within white blood cells called macrophages.
It's important to understand that the body tightly regulates the different forms as it might a steroid. 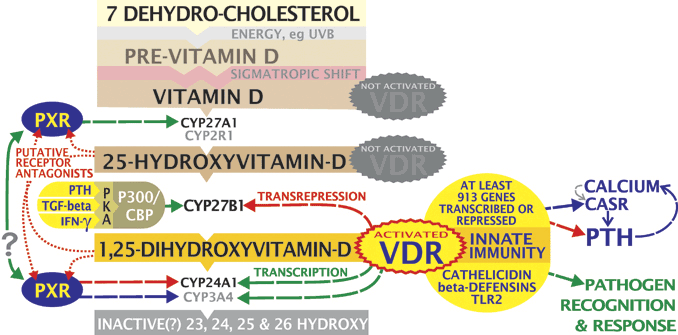 Metabolism of vitamin D and the Vitamin D Receptor
Metabolism of vitamin D and the Vitamin D Receptor A number of studies have suggested that patients with chronic inflammatory diseases are deficient in
25-hydroxyvitamin-D (25-D) and that consuming greater quantities of vitamin D, which elevates 25-D levels, alleviates symptoms of disease. Some years ago, molecular biology identified 25-D as a secosteroid. Secosteroids would typically be expected to depress
inflammation, which is in line with the reports of symptomatic improvement. The simplistic first-order mass-action model used to guide the early vitamin studies has given way to a more complex description of action. When active, the
Vitamin D nuclear receptor (VDR) affects transcription of at least 913 genes and impacts processes ranging from calcium metabolism to expression of key
antimicrobial peptides.
Located in the nucleus of a variety of cells including immune cells, the VDR is a control system of sorts. When exposed to infection and damage, especially that which is caused by pathogens, the body begins to convert the inactive form 25-D into the active form,
1,25-D. As cellular concentrations of 1,25-D increase, 1,25-D activates the VDR, turning on any number of genes the receptor transcribes.
According to a 2010 analysis, the VDR significantly affects 229 human genes. Many of these genes have long been associated with
autoimmune diseases and
cancers including, for example, the genes IRF8 (linked to
multiple sclerosis), and PTPN2 (connected to
Crohn's disease and type I
diabetes).
1 The activation of certain genes also leads to the synthesis of antimicrobial peptides. The antimicrobial peptides are the body's “natural antibiotics” and have a potent anti-bacterial effect.
However, bacteria create ligands, which like 25-D, inactivate the VDR and, in turn, the
innate immune response. This allows the microbes to proliferate. In response, the body increases production of 1,25-D from 25-D, leading to one of the hallmarks of chronic inflammatory disease: a low 25-D and a high 1,25-D.
This pattern is a result of the disease process rather than a cause. For a variety of reasons, neither increased consumption of vitamin D nor the body's synthesis of additional 1,25-D is ultimately effective at combatting infection.
Supplemental Vitamin D tends to be immunosuppressive Supplemental vitamin D has been widely lauded for conferring immunosuppressive effects.
Vitamin D affects the immune system at many levels and by a number of mechanisms…. Vitamin D has multiple immunosuppressant properties…. On the whole, vitamin D confers an immunosuppressive effect.
Aronson, Amital, and Shoenfeld 2
Examples of vitamin D's immunosuppressant effects include:
Epstein Barr virus – In a 2010 study of pregnancy-associated breast cancer, higher levels of 25-D were positively correlated with serum antibodies to Epstein Barr Virus, suggesting that EBV is able to better proliferate in patients who take vitamin D.3toll-like receptors – As discussed elsewhere, the toll-like receptors (TLR) represent an ancient front-line defense system that enables the host organism to sense the presence of microbial components within minutes. As inducers of inflammation, TLRs act as important triggers of distinct entities such as sepsis or autoimmune disease exacerbation.4 For example, found that the TLRs are naturally upregulated in the autoimmune disease, Behcet's disease.5 However, a 2006 study showed that vitamin D3 suppresses the expression of TLR2 and TLR4 protein and mRNA in human monocytes in a time- and dose-dependent fashion.6Dickie et al. further showed that expression of TLR9 was downregulated in monocytes by vitamin D3 supplementation.7
short-term symptom resolution – Further evidence for vitamin D’s activity as an immunosuppressant comes in the range of reports of short-term symptom resolution in autoimmune patients taking vitamin D. Online forums are full of such reports.
Role in select diseases and conditions The following articles discuss the role of vitamin D in select diseases. A more
complete list of diseases that have been shown to have low level of 25-D is also available.
Osteoporosis Both
osteoporosis and osteopenia are diseases marked by a decrease in bone mineral density. Osteopenia is a less severe form of and sometimes precursor to osteoporosis. The loss of bone mass leads to a porous bone structure, frequent fractures, and delayed healing.
Among doctors, and even many researchers, it is conventional wisdom that vitamin D supplementation reverses osteopenia and osteoporosis. However, a growing body of interventional trials and molecular evidence shows this is not the case. Instead, current research has demonstrated that osteoporosis and osteopenia are often the direct result of infection with the
Th1 pathogens, a
metagenomic microbiota, which produce inflammatory
cytokines and inactivate the Vitamin D Receptor. The only way to achieve long-term reversal of bone loss is to kill the Th1 pathogens driving the disease process.
Rickets Rickets (osteomalacia) is a softening of the bones that leads to fractures and deformity. The majority of cases of rickets occur among children in developing countries who suffer from severe malnutrition. The disease is cited as a primary reason for consuming
vitamin D regularly even though research has demonstrated that rickets is not caused by vitamin D deficiency but by hypophosphatemia.
The latest molecular evidence does not support adding high levels of vitamin D to the food chain in the name of “preventing rickets.” The health of the public would be much better served by regulations ensuring that they obtain adequate calcium and phosphorous rather than vitamin D.
Cancer A variety of studies have suggested that vitamin D protects against cancer. This seemingly intuitive proposition is supported by neither epidemiological nor molecular evidence. In fact, the very opposite is true. This article reviews why this body of research is most likely incorrect – or at the very least, much more complicated than articles in the popular media would have a person believe.
Latitude studies - The “latitude studies” are observational, as opposed to interventional, studies, which use ambient solar UV radiation as a proxy for latitude and vitamin D status. For these studies, researchers compare rates of certain major cancers - most notably breast, colorectal and prostate cancer - to rates of sunlight exposure. This group of research has the liability of being wildly inconsistent. The choice to publish research on a specific latitude gradient may be a better proxy for a researcher's bias.
Interventional studies - While some randomized controlled trials have suggested that consuming vitamin D reduces rates of cancer, larger and more carefully controlled studies show no such effect.
Studies of vitamin D status - Many of the studies examining the relationship between vitamin D status and incidence of cancer argue that low levels of 25-D contribute to cancer. This conclusion has been invalidated by larger well-controlled studies. Although the immune system works to downregulate 25-D (25-hydroxyvitamin D) in inflammatory diseases such as cancer, very high levels of 25-D are a clear indication of regular supplementation. These studies suggest that consuming large amounts of vitamin D predispose a person to increased incidence of cancer.
Observational studies – Some case control studies have found that vitamin D intake seems to increase incidence of certain types of cancer.
Cardiovascular disease According to a 2010 paper by Swales and Wang, “despite substantial clinical evidence linking vitamin D deficiency with increased cardiovascular risk, it remains to be established whether this represents a causal association.”8A recent cross-sectional study involving 340 African Americans with type 2 diabetes found that serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels were positively associated with increased calcified atherosclerotic plaque in the aorta and carotid arteries.9 Depression and seasonal affective disorder According to the Marshall Pathogenesis, light-related changes in mood can be attributed to fluctuations in 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D (1,25-D). Such reactions exist in people who suffer from “
seasonal affective disorder” as well as those who are addicted to or dependent upon tanning.
Contrary to popular belief, epidemiological research points to an
increase in suicide across countries during the beginning of the summer months when people tend to get more light exposure.
Light exposure does nothing to resolve underlying disease state and can actually delay progress for Marshall Protocol (MP) patients. Certainly prolonged light exposure has been shown to increase skin melanoma – the World Health Organization now categorizes tanning beds under the highest cancer risk category.
10MP patients who have completed the treatment have been able to attest to the fact that sunshine is not necessary for good health or happiness.
Despite what some researchers have argued,
latitude studies that try to tie ambient solar UV radiation to prevalence of disease have been inconclusive.
Pregnancy 1,25-D rises by 40% in the early pregnant decidua, meaning that its ability to dysregulate the nuclear receptors and the antimicrobial peptides (AmPs) they express is particularly prevalent during the first trimesters of pregnancy. The subsequent decrease in immune function slows immunopathology, resulting in symptomatic relief. But when the surge in 1,25-D disappears after pregnancy, AmP expression and immunopathology increase once again, leading to exacerbation of disease symptoms. This may explain why some women with autoimmune disease experience periods of palliation during gestation only to become increasingly symptomatic after giving birth.
Problems with some Vitamin-D Research... Insufficient followup in vitamin D studies One of the abiding weaknesses of studies on the effects of vitamin D on health is that researchers simply do not follow subjects consuming the secosteroid for a sufficient period of time. Instead, they tend to track subjects over the course of weeks, months, or one or two years, during the period of time when study participants are usually feeling the palliative effects of the steroid. This practice is a mistake as it does not account for the long-term immunosuppressive effects of a steroid.
Falling to control for biases inherent to observational studies It is arguably impossible to sufficiently control for the socioeconomic factors, which drive a person to participate in a therapy or take a supplement. The case of hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is instructive. For decades, researchers thought that HRT prevented disease, but it was ultimately shown that it caused it.
Studies of vitamin D's efficacy are especially fraught with challenges. For one, the secosteroid is palliative and the negative side effects can only be seen after decades of use. Also, people who take vitamin D are demonstrably different than those who don't. They almost always have a higher socioeconomic status.
Not all studies on vitamin D's efficacy are observational, but those that are may warrant a special amount of skepticism.
Mistaking correlation for causation Many vitamin D studies suffer from methodological errors including
bias inherent to using self-selected subjects and
insufficient followup, but perhaps their most egregious liability comes in mistaking correlation for causation.
It's undisputed that a wide array of studies point to the fact that 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25-D) – typically referred to in the media as vitamin D – is low in people with numerous chronic inflammatory diseases. However, these studies fail to prove that low 25-D
causes disease.
In fact, molecular science has revealed that the levels of the vitamin D metabolites through a
series of intricate and carefully controlled feedback pathways, mechanisms that belie the simplistic first-order mass-action model used to guide the short-sighted vitamin studies. Also, epidemiological evidence suggests that while 25-D is low in chronic disease, 1,25-D (1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D) tends to be very high, an observation which is at odds with the theory that vitamin D deficiency causes or exacerbates disease.
There have been lots of observational studied showing an association between various diseases and vitamin D deficiency, but there is not any evidence yet that that is a casual relationship… it may be that vitamin D deficiency is a marker of ill health.
Dr. Ruth McQuillan, University of Edinburgh Populations that avoid vitamin D remain healthy despite low levels of 25-D According to Professor Roger Bouillon of the University of Leuven, “over one billion” people worldwide need to increase their vitamin D intake due to vitamin D “deficiency.”
11 One Saudi study
concluded that 87.8% of healthy men were “deficient.”
Yet, observational studies show that populations which avoid vitamin D consumption have naturally low levels of 25-D and remain healthy with such levels.
healthy Chilean women – A study which tested the level of 25-D in 90 “healthy, ambulatory Chilean women” showed that 27% of the premenopausal and 60% of the postmenopausal women had 25-D levels under 20 ng/ml.12
healthy Bangladeshi women – A study on healthy Bangladeshi women found that approximately 80% of the women had a level of 25-D under 16 ng/ml.13
healthy Chinese infants – In a 1992 study, healthy full-term infants from China had serum concentrations of 25-D ranging from an average of 5 ng/ml to 14 ng/ml.14
healthy Omani women – A 2011 study of 41 apparently healthy women (ages 18-45 years) working at the Royal Hospital, Muscat, Oman found that all study subjects had 25-D levels below 50 nmol/L.15
young healthy adults in western India – Among young healthy adults from the western part of India, the average serum level of 25-D indicated vitamin D “deficiency”: 17.4 ng/ml.16
healthy Saudi Arabians – Severe hypovitaminosis D is widespread and more common in non-diabetics than diabetics in Saudi adults.17Nevertheless, this 2010 study's authors conclude a bit bizarrely, “The study further underscores the need for vitamin D fortification of the Saudi diet, and the promotion of vitamin D supplementation in both groups.”
healthy lactating mothers – Even when lactating mothers take all but exceedingly high levels of vitamin D – 6,000 IU which is 15 times the United States' Recommended Daily Intake – the vitamin D content in breast milk remains very low.18 This is confusing for advocates of vitamin D supplementation who would think that breastfeeding mothers would give their infantextra levels of vitamin D during formative stages of growth.
The Vitamin D Council, an organization that advocates vitamin D supplementation,
states:
One of the great mysteries in human biology is the fact that most human breast milk is deficient in vitamin D. How could Nature overlook such an important nutrient in the “perfect food”?
Vitamin D Council
One research team, studying patients with xeroderma pigmentosum, a genetic disorder in which patients are unable to repair damage caused by ultraviolet light, found that vitamin D levels are maintained even when patients practice at least six years of rigorous photoprotection and not supplementing with vitamin D. More importantly, the researchers also concluded that the clinical manifestations of vitamin D “deficiency” were absent.
The patients all wore protective clothing and sunscreens when outdoors. Estimated mean vitamin D intake was normal. The mean values of serum 25-OHD were low normal, but 1,25-(OH)2D, calcium, ionized calcium and parathyroid hormone levels were normal[italics added]…. Despite rigorous sun protection normal vitamin D levels can be maintained in ambulatory patients with XP.
Armando Sallitto et al.19
Ramifications of a simplistic understanding of vitamin D metabolism Numerous studies have identified patient populations that are “deficient” in vitamin D. Patients suffering from
obesity,
schizophrenia,
fibromyalgia,
multiple sclerosis,
autism, etc. all seem to be suffering from vitamin D deficiency. One could list
hundreds of such studies.
Although it is not unheard of, few seem to explore the possibility that a low 25-D is the result of disease. Perhaps it is because researchers conceptualize vitamin D as they might a resource which gets used up and needs to be replenished – not unlike gasoline when a car runs low. This metaphor is not at all apt, because vitamin D is regulated like the steroid it is.
20 21Large segments of the population are consuming vitamin D at historic levels. Like the first-line treatment for many autoimmune diagnoses, the
corticosteroid Prednisone, vitamin D temporarily reduces symptoms of disease, but long-term use dramatically increases the odds of disease relapse.
22In practice, widespread and systematic supplementation of vitamin D may serve to drive a kind of self-fulfilling prophesy. When whole populations are given large amounts of vitamin D, the only members of that population who remain “deficient” are those whose immune systems are fighting disease by actively downregulating 25-D. In other words, the more rigorously vitamin D is added to milk, juice, snack bars, and breakfast cereals, the less likely it is that someone has low levels of vitamin D but no chronic disease.
Supplemental vitamin D given to healthy people According to the Marshall Pathogenesis, limited amounts of vitamin D
may be helpful for a time to healthy people. Because the body is able to properly regulate the VDR, ingested vitamin D is rapidly converted into 1,25-D, which activates the VDR. This may explain the one (barely) significant finding from a 2011 Cochrane systematic review.
23 (
Publication bias may have also tilted the findings towards intervention.) However, this is certainly no basis for forced fortification.
Marshall Protocol and vitamin D As opposed to certain treatments which employ
sunshine or light therapy, patients on the
Marshall Protocol (MP) use the
VDR agonist,
olmesartan, and pulsed, low-dose antibiotics to gradually eliminate the Th1 pathogens. Patients on the treatment must refrain from supplementing with vitamin D or eating any foods that contain vitamin D. These measures allow 25-D levels to drop to a point where the VDR can most optimally activate the innate immune system.
Because the vitamin D metabolites are dysregulated in chronic disease, most patients on the MP also become sensitive to light. Although light sensitivity improves as the Th1 pathogens are killed, most patients must avoid bright sunlight and block bright light in the eyes with special sunglasses during the healing process. However, once the Th1 pathogens have been killed and the vitamin D metabolites have re-stabilized, patients are able to tolerate sunlight and bright lights once again.
References 1. Ramagopalan SV, Heger A, Berlanga AJ, Maugeri NJ, Lincoln MR, Burrell A, Handunnetthi L, Handel AE, Disanto G, Orton SM, Watson CT, Morahan JM, Giovannoni G, Ponting CP, Ebers GC, Knight JC
A ChIP-seq defined genome-wide map of vitamin D receptor binding: associations with disease and evolution. Genome Res. 2010;20:1352-60.
2. Arnson Y, Amital H, Shoenfeld Y
Vitamin D and autoimmunity: new aetiological and therapeutic considerations. Ann Rheum Dis. 2007;66:1137-42.
3. Agborsangaya CB, Lehtinen T, Toriola AT, Pukkala E, Surcel HM, Tedeschi R, Lehtinen M
Association between Epstein-Barr virus infection and risk for development of pregnancy-associated breast cancer: Joint effect with vitamin D? Eur J Cancer. 2010;:.
4. ,
6. Sadeghi K, Wessner B, Laggner U, Ploder M, Tamandl D, Friedl J, Zügel U, Steinmeyer A, Pollak A, Roth E, Boltz-Nitulescu G, Spittler A
Vitamin D3 down-regulates monocyte TLR expression and triggers hyporesponsiveness to pathogen-associated molecular patterns. Eur J Immunol. 2006;36:361-70.
5. Do JE, Kwon SY, Park S, Lee ES
Effects of vitamin D on expression of Toll-like receptors of monocytes from patients with Behcet's disease. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2008;47:840-8.
7. Dickie LJ, Church LD, Coulthard LR, Mathews RJ, Emery P, McDermott MF
Vitamin D3 down-regulates intracellular Toll-like receptor 9 expression and Toll-like receptor 9-induced IL-6 production in human monocytes. Rheumatology (Oxford).2010;49:1466-71.
8. Swales HH, Wang TJ
Vitamin D and cardiovascular disease risk: emerging evidence. Curr Opin Cardiol. 2010;22:513-7.
9. Freedman BI, Wagenknecht LE, Hairston KG, Bowden DW, Carr JJ, Hightower RC, Gordon EJ, Xu J, Langefeld CD, Divers J
Vitamin d, adiposity, and calcified atherosclerotic plaque in african-americans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010;95:1076-83.
10. El Ghissassi F, Baan R, Straif K, Grosse Y, Secretan B, Bouvard V, Benbrahim-Tallaa L, Guha N, Freeman C, Galichet L, Cogliano V
A review of human carcinogens--part D: radiation. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10:751-2.
11. Boullion, R. (2006 April 2).
Vitamin D analogues: pharmacology and therapeutic uses. European Congress of Endocrinology, Glasgow.
12. González G, Alvarado JN, Rojas A, Navarrete C, Velásquez CG, Arteaga E
High prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in Chilean healthy postmenopausal women with normal sun exposure: additional evidence for a worldwide concern. Menopause.2007;14:455-61.
13. Islam MZ, Akhtaruzzaman M, Lamberg-Allardt C
Hypovitaminosis D is common in both veiled and nonveiled Bangladeshi women. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2006;15:81-7.
14. Specker BL, Ho ML, Oestreich A, Yin TA, Shui QM, Chen XC, Tsang RC
Prospective study of vitamin D supplementation and rickets in China. J Pediatr. 1992;120:733-9.
15. Al-Kindi MK
Vitamin D Status in Healthy Omani Women of Childbearing Age: Study of female staff at the Royal Hospital, Muscat, Oman. Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J. 2011;11:56-61.
16. Shivane VK, Sarathi V, Bandgar T, Menon P, Shah NS
High prevalence of hypovitaminosis D in young healthy adults from the western part of India. Postgrad Med J. 2011;:.
17. Al-Daghri NM, Al-Attas OS, Al-Okail MS, Alkharfy KM, Al-Yousef MA, Nadhrah HM, Sabico SB, Chrousos GP
Severe hypovitaminosis D is widespread and more common in non-diabetics than diabetics in Saudi adults. Saudi Med J. 2010;31:775-80.
18. Wagner CL, Hulsey TC, Fanning D, Ebeling M, Hollis BW
High-dose vitamin D3 supplementation in a cohort of breastfeeding mothers and their infants: a 6-month follow-up pilot study. Breastfeed Med. 2006;1:59-70.
19. Sollitto RB, Kraemer KH, DiGiovanna JJ
Normal vitamin D levels can be maintained despite rigorous photoprotection: six years' experience with xeroderma pigmentosum. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997;37:942-7.
20. Moan J, Lagunova Z, Lindberg FA, Porojnicu AC
Seasonal variation of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D and its association with body mass index and age. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2009;113:217-21.
21. Schwartz JB
Effects of vitamin D supplementation in atorvastatin-treated patients: a new drug interaction with an unexpected consequence. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2009;85:198-203.
22. Gottlieb JE, Israel HL, Steiner RM, Triolo J, Patrick H
Outcome in sarcoidosis. The relationship of relapse to corticosteroid therapy. Chest. 1997;111:623-31.
23. Bjelakovic G, Gluud LL, Nikolova D, Whitfield K, Wetterslev J, Simonetti RG, Bjelakovic M, Gluud C
Vitamin D supplementation for prevention of mortality in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011;7:CD007470.
24. Goswami R, Gupta N, Goswami D, Marwaha RK, Tandon N, Kochupillai N
Prevalence and significance of low 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations in healthy subjects in Delhi. Am J Clin Nutr. 2000;72:472-5.
25. Crew KD, Shane E, Cremers S, McMahon DJ, Irani D, Hershman DL
High prevalence of vitamin D deficiency despite supplementation in premenopausal women with breast cancer undergoing adjuvant chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:2151-6.
26. Wjst M
Introduction of oral vitamin D supplementation and the rise of the allergy pandemic. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol.2009;5:8.
Edited by hallucinogen, 14 September 2011 - 06:47 AM.


![]()