So, everything is in the title. Suggest science based supplements or drugs that reduce amygdala reactivity to fearful stimuli. One of them is modafinil. The other one probably alcohol, but it also impairs judgement.

Decrease amygdala reactivity to fearful stimuli with supplements or drugs
#1
Posted 22 March 2020 - 01:00 AM
#2
Posted 22 March 2020 - 07:51 AM
sponsored ad
#3
Posted 22 March 2020 - 01:05 PM
Thank you for your response. Are there any crf1 antagonists that aren't regulated pharmaceutical drugs?
EDIT: oxytocin might be good for decreasing amygdala reactivity to fearful stimuli
Edited by Starchild1337, 22 March 2020 - 01:07 PM.
#4
Posted 22 March 2020 - 04:21 PM
yes valproic acid and lithium carbonate. there are also specific made crf1 antagonists like antalarmin but those are harder to get.
https://www.ncbi.nlm...pubmed/12606697
When you say regulated did you mean like adderall or just all pharma drugs? if second, ignore the message above. I made a huge crf1 antagonist thread if you can stomach going trough it because I ramble a lot but it has some info on various substances which block crhr1 or crh that aren't pharma drugs but supplements otc.
(edit) link https://www.longecit...f1-antagonists/
Edited by kurdishfella, 22 March 2020 - 05:14 PM.
#5
Posted 22 March 2020 - 04:24 PM
Yeah, I meant non-prescription substances because it's hard convincing doctors that you need something that reduces fear but not an SSRI. You can link the thread.
Is that the same lithium that people use for mood or bipolar? I tried it and it actually made me more emotionally unstable.
#7
Posted 22 March 2020 - 05:12 PM
Been using Omega3 and vitamin D for years. Never noticed any effects on reducing fear.
#8
Posted 23 March 2020 - 01:56 AM
fear of what
#9
Posted 23 March 2020 - 01:37 PM
fear of what
Fear of life in general, taking risks, public speaking, coming up to strangers, trying new things. I just feel incredibly inhibited even though I don't want to be, but I think it's genetic. My mom is a similar person, but you can't live life like that. Modafinil is one of the rare things that sets me free and makes me take risks socially. I googled and found one study saying it does this to the amygdala.
#10
Posted 23 March 2020 - 02:36 PM
Modafinil activates orexin which would increase amygdala activity. A lot of people think they have chemical imbalance or their mental disorder is due to genetics but is it really?
These findings demonstrate the circuit involving orexin, NALC and LA neurons mediates fear-related behavior and suggests inappropriate excitation of this pathway may cause fear generalization sometimes seen in psychiatric disorders, such as PTSD. https://www.nature.c...467-017-01782-z
#11
Posted 23 March 2020 - 06:49 PM
Modafinil in low doses has a unique physiologic profile compared with stimulant drugs: it enhances the efficiency of prefrontal cortical cognitive information processing, while dampening reactivity to threatening stimuli in the amygdala, a brain region implicated in anxiety. (100 mg/day)
https://www.ncbi.nlm...les/PMC3013347/
#12
Posted 23 March 2020 - 08:01 PM
https://www.ncbi.nlm...les/PMC3612440/
If you must use a supplement...
#13
Posted 23 March 2020 - 09:00 PM
Lavender (inhaled or rubbed into the skin).
https://www.ncbi.nlm...les/PMC3612440/
If you must use a supplement...
Thank you. It doesn't have to be just supplements, but they are much easier to acquire.
sponsored ad
#14
Posted 27 March 2020 - 05:45 PM
Seems like inhibiting the adrenaline and epinephrine response would also help. Modulating serotonin often fixes a myriad of problems because it is upstream of literally everything. See serotonin signalling map (attachment #1). Interestingly, I've included a study where Tyrosine (which eventually leads to adrenaline synthesis) where the fear response was also reduced. I don't know, sometimes moderation is key.
Korean Red Ginseng prevents posttraumatic stress disorder–triggered depression-like behaviors in rats via activation of the serotonergic system
Daily KRG administration significantly improved depression-like behaviors in the forced swimming test, increased the number of lines crossed and time spent in the central zone in the open field test, and decreased freezing behavior in contextual and cued fear conditioning. KRG treatment attenuated SPS-induced decreases in serotonin (5-HT) tissue concentrations in the hippocampus and medial prefrontal cortex. The increased 5-HT concentration during KRG treatment may be partially attributable to the 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid/5-HT ratio in the hippocampus of rats with PTSD. These effects may be caused by the activation of hippocampal genes encoding tryptophan hydroxylase-1 and 2 mRNA levels.
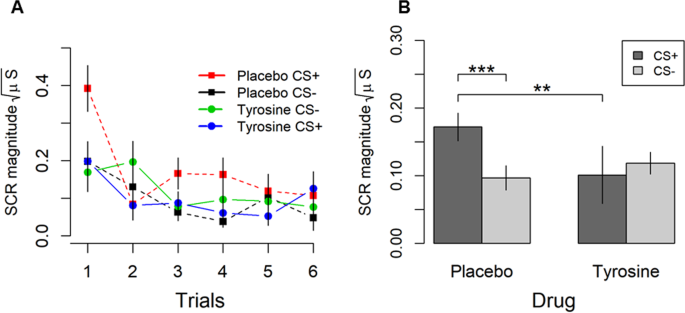
Here, we sought to determine if putative increases in presynaptic dopamine and norepinephrine by tyrosine administered before conditioning could affect fear expression. Electrodermal activity (EDA) of 46 healthy participants (24 placebo, 22 tyrosine) was measured in an instructed fear task. Results showed that tyrosine abolished fear expression compared to placebo. Importantly, tyrosine did not affect EDA responses to the aversive stimulus (UCS) or alter participants’ mood. Therefore, the effect of tyrosine on fear expression cannot be attributed to these factors. Taken together, these findings provide evidence that the catecholaminergic system influences fear expression in humans.
Effect of Korean Red Ginseng in individuals exposed to high stress levels: a 6-week, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial
Results
At baseline, both groups showed no significant differences in age, sex, years of education, Beck Depression Inventory, and Stress Response Inventory. After 6 weeks, triglyceride levels were significantly increased within the normal limit in theKorean Red Ginseng group (F = 4.11, p = 0.048), and the epinephrine level was decreased in this group (F = 4,35, p = 0.043). The triglyceride increase was significantly associated with epinephrine decrease (B = −0.087, p = 0.041), suggesting that Korean Red Ginseng may stabilize the sympathetic nervous system. In addition, we detected a significant group by time effect in the visually controlled continuous performance test, suggesting positive effects of Korean Red Ginseng on cognition.
Conclusion
Korean Red Ginseng might help to stabilize the sympathetic nervous system and improve cognition in individuals with high stress.
Attached Files
Also tagged with one or more of these keywords: mental health, brain
1 user(s) are reading this topic
0 members, 1 guests, 0 anonymous users